● Class 9th NCERT Science Solutions Chapterwise
Chapter 03. Atoms and Molecules
CHAPTER 03 solutions in english medium Best wishes by Nitish sir 🤞🤞
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules
Page 27, 28
Question 1. In a reaction 5.3 g of sodium carbonate reacted with 6 g of ethanoic acid. The products were 2.2 g of carbon dioxide, 0.9 g water and 8.2 g of sodium acetate. Show that these observations are in agreement with the law of conservation of mass carbonate.
Answer:
Question 2. Hydrogen and oxygen combine in the ratio of 1 : 8 by mass to form water. What mass of oxygen gas would be required to react completely with 3 g of hydrogen gas?
Question 3. Which postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory is the result of the law of conservation of mass?
Answer: The postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory that is the result of the law of conservation of mass is—the relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound. Atoms cannot be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Question 4. Which postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory can explain the law of definite proportions?
Answer: The relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound.
Page 30
Question 1. Define the atomic mass unit.
Answer: One atomic mass unit is equal to exactly one-twelfth (1/12th) the mass of one atom of carbon-12. The relative atomic masses of all elements have been found with respect to an atom of carbon-12.
Question 2. Why is it not possible to see an atom with naked eyes?
Answer: Atom is too small to be seen with naked eyes. It is measured in nanometres.
1 m = 109 nm
Page 34
Question 1. Write down the formulae of
(i) Sodium oxide
(ii) Aluminium chloride
(iii) Sodium sulphide
(iv) Magnesium hydroxide
Answer: The formulae are
Question 2. What is meant by the term chemical formula?
Answer: The chemical formula of the compound is a symbolic representation of its composition, e.g., chemical formula of sodium chloride is NaCl.
Question 3. How many atoms are present in a
(i) H2S molecule and
(ii) P043- ion?
Answer:
(i) PO43− ion has 4 oxygen atoms and 1 phosphorus atom. So, a total of 5 atoms.
(ii) H2S molecule has 1 sulphur and 2 hydrogen atoms. So, a total of 3 atoms.
Page 35
Question 1. Calculate the molecular masses of H2, O2, Cl2, C02, CH4, C2H2,NH3, CH3OH.
Answer: The molecular masses are: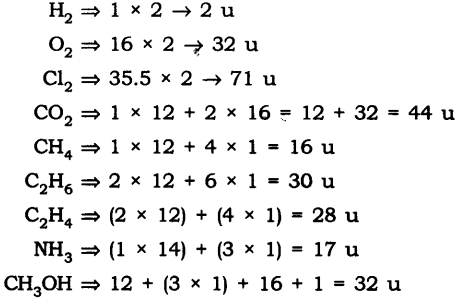
Question 2.Calculate the formula unit masses of ZnO, Na2O, K2C03, given atomic masses of Zn = 65 u, Na = 23 u, K = 39 u, C = 12 u, and O = 16 u.
Answer: The formula unit mass of
(i) ZnO = 65 u + 16 u = 81 u
(ii) Na2O = (23 u x 2) + 16 u = 46 u + 16 u = 62 u
(iii) K2C03 = (39 u x 2) + 12 u + 16 u x 3
= 78 u + 12 u + 48 u = 138 u
EXERCISE QUESTIONS PAGE- 36
Question 1. A 0.24 g sample of compound of oxygen and boron was found by analysis to contain 0.096 g of boron and 0.144 g of oxygen. Calculate the percentage composition of the compound by weight.
Answer - SolutionTotal mass of compound = 0.24 g (given)
Mass of boron = 0.096 g (given)
Mass of oxygen = 0.144 g (given)
Percent composition of compond:[ GivenmassofelementTotalmassofcompound×100]%
Thus, percentage of boron by weight in the compound
=0.0960.24×100% =40%
And, percentage of oxygen by weight in the compound
=0.1440.24 ×100%=60%
QUESTION 2. When 3.0 g of carbon is burnt in 8.00 g oxygen, 11.00 g of carbon dioxide is produced. What mass of carbon dioxide will be formed when 3.00 g of carbon is burnt in 50.00 g of oxygen? Which law of chemical combination will govern your answer?
If 3 g of carbon is burnt in 50 g of oxygen, then 3g of carbon will react only with 8g of oxygen and 42 g of oxygen remains unreacted.
Thus, 11.00 g of carbon dioxide is produced.
Question 3. What are polyatomic ions? Give examples
Answer: Polyatomic ions are ions which consist of more than one atom. For example, nitrate ion, NO3-, contains one nitrogen atom and three oxygen atoms.
(a) Magnesium chloride
(b) Calcium oxide
(c) Copper nitrate
(d) Aluminium chloride
(e) Calcium carbonate.
| Compound | Chemical Formula | Elements present |
|---|---|---|
| Quick lime | CaO | Calcium, Oxygen |
| Hydrogen bromide | HBr | Hydrogen, Bromine |
| Baking powder | NaHCO3 | Sodium, Hydrogen, Carbon, Oxygen |
| Potassium sulphate | K2SO4 | Potassium, Sulphur, Oxygen |
Molar mass of ethyne = 2 x 12 + 2 x 1
Molar mass of ethyne = 26 g
(b) Chemical formula of Sulphur molecule S8
Molar mass of sulphur molecule = 8 x 32 = 256 g
(c) Chemical formula of Phosphorus molecule, P4 (atomic mass of phosphorus = 31)
Molar mass of phosphorus molecule = 4 x 31 = 124 g
(d) Chemical formula of Hydrochloric acid HCl
Molar mass of hydrochloric acid = 1 + 35.5 = 36.5 g
(e) Chemical formula of Nitric acid HNO3
Molar mass of nitric acid = 1 + 14 + 3 x 16 = 63 g




Comments
Post a Comment