NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control And Coordination
by NITISH SIR, CBSE
NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control And Coordination are part of NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control And Coordination.
NCERT Exemplar Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Control And Coordination
Short Answer Type Questions
1.Label the parts (a), (b), (c) and (d) and show the direction of flow of electrical signals in the given figure.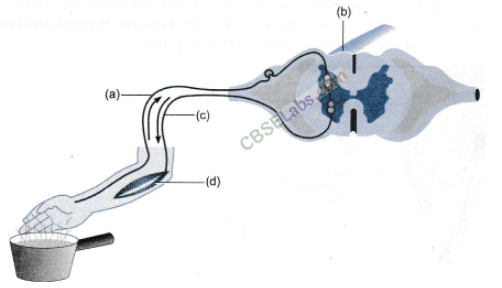
Answer.
(a) Sensory neuron.
(b) Spinal cord (CNS).
(c) Motor neuron.
(d) Effector (Muscle in arm).
2.Name the plant hormones responsible for the following:
(а) Elongation of cells.
(b) Growth of stem.
(c) Promotion of cell division.
(d) Falling of senescent leaves.
Answer.(a) Auxin. (b) Gibberellin. (c) Cytokinin. (d) Abscisic acid.
3.Label the endocrine glands in the given figure.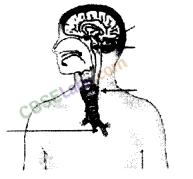
Answer.(a) Pineal gland. (b) Pituitary gland, (c) Thyroid, (d) Thymus.
4 What is a tropic movement? Explain with an example.
Answer.The directional growth movements of plants due to external stimuli are called tropic movement. It can be either towards the stimulus, or away from it. For example, in case of phototropic movement, shoots respond by bending towards light while roots respond by bending away from it.
5.What will happen if intake of iodine in our diet is low?
Answer.When iodine intake is low, release of thyroxin from thyroid gland will be less by which protein, carbohydrate and fat metabolisms will be affected.
A person might suffer from goitre in case of iodine deficiency in the body,
6.Answer the following:
(а) Which hormone is responsible for the changes noticed in females at puberty?
(b) Dwarfism results due to deficiency of which hormone?
(c) Blood sugar level rises due to deficiency of which hormone?
(d) Iodine is necessary for the synthesis of which hormone?
Answer.(a) Oestrogen. (b) Growth hormone. (c) Insulin. (d) Thyroxin.
7.Answer the following:
(a) Name the endocrine gland associated with brain?
(b) Which gland secretes digestive enzymes as well as hormones?
(c) Name the endocrine gland associated with kidneys?
(d) Which endocrine gland is present in males but not in females?
Answer.(a) Pituitary. (b) Pancreas, (c) Adrenal. (d) Testes.
Long Answer Type Questions
8.What are the major parts of the brain? Mention the functions of different parts.
Answer.
• Forebrain: It is composed of the cerebrum.
• Midbrain: It is composed of the hypothalamus.
• Hindbrain: It is composed of the cerebellum, pons and medulla oblongata.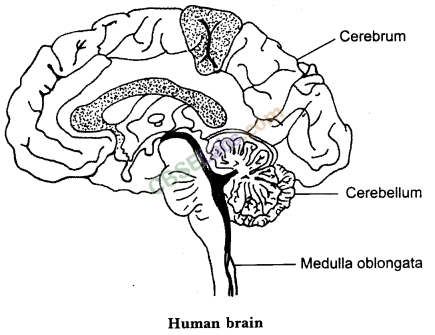
Some main structures of the human brain are explained below.
(i) Cerebrum: The cerebrum is the largest part in the human brain. It is divided into two hemispheres; called cerebral hemispheres.
Functions of cerebrum:
(a) The cerebrum controls the voluntary motor actions.
(b) It is the site of sensory perceptions; like tactile and auditory perceptions.
(c) It is the seat of learning and memory.
(ii) Hypothalamus: The hypothalamus lies at the base of the cerebrum. It controls sleep and wake cycle (circadian rhythm) of the body. It also controls the urges for eating and drinking.
(iii) Cerebellum: Cerebellum lies below the cerebrum and at the back of the whole structure. It coordinates the motor functions. When you are riding your bicycle; the perfect coordination between pedaling and steering control is achieved by the cerebellum.
(iv) Medulla: Medulla forms the brain stem; along with the pons. It lies at the base of the brain and continues into the spinal cord. Medulla controls various involuntary functions; like heart beat, respiration, etc.
9.Mention one function for each of these hormones:
(a) Thyroxin (b) Insulin (c) Adrenaline (d) Growth hormone (e) Testosterone.
Answer. (a) Thyroxin regulates carbohydrate, fat and protein metabolisms.
(b) Insulin regulates blood sugar.
(c) Adrenaline increases heart rate and supply of blood to various organs.
(d) Growth hormone regulates growth and development.
(e) Testosterone controls the changes of body features associated with puberty in male.
10. Name various plant hormones. Also give their physiological effects on plant growth and development.
Answer. The various plant hormones are Auxin, Gibberellin,Cytokinin, and Abscisic acid. Their physiological effects on plant growth are as follows:
Auxins: Cell elongation, cell division, root formation, apical dominance, inhibition of abscission and fruit growth.
Gibberellins: Growth in stem and leaves, higher fruit yield and over coming dormancy.
Cytokines: Promotes cell division, differentiation, prevention of senescence and overcoming apical dominance .
Absciscic acid: Induces dormancy, senescence, abscission, checking excessive activity of growth promoting hormone and closure of stomata under water stress. .
11. Why is the flow of signals in a synapse from axonal end of one neuron to dendritic end of another neuron but not the reverse?
Answer. When an electrical signal reaches the axonal end of a neuron, it releases a chemical substance. This chemical diffuses towards the dendrite end of next neuron where it generates an electrical impulse or signal. Hence, the electrical signal is converted into a chemical signal at the axonal end. Since these chemicals are absent at the dendrite end of the neuron the electrical signal, cannot be converted into chemical signal.
Comments
Post a Comment